Introduction to Natural Numbers
Natural numbers are the fundamental building blocks of mathematics, representing the simplest form of counting. They are whole, positive numbers, starting from 1 and extending infinitely. In mathematical notation, the set of natural numbers is denoted by the symbol ℕ. They are also called as Counting Numbers.
What Are Natural Numbers?
Natural numbers are the counting numbers that start from 1 and go on infinitely: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so forth. Natural numbers are the foundation of mathematics, and they’re essential for understanding the world around us.
Note:Natural Numbers do not contain zero (0) or negative numbers.
Natural Numbers Definition?
Natural numbers are the set of whole, positive numbers used for counting and ordering, beginning with 1 and extending infinitely.The set of Natural Numbers is denoted by Capital letter ‘N’
Symbolically N={1, 2, 3…}
Note: The Smallest Natural Number is 1. There is no largest Natural Number.

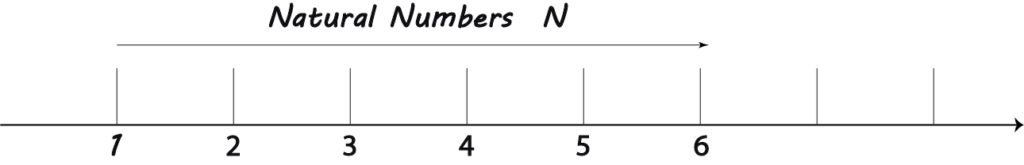
Natural Numbers on a Number line
The natural number line is a fundamental mathematical concept representing the sequence of positive integers extending infinitely.
On a number line, these numbers are typically represented by evenly spaced points or tick marks along a straight line. Each point or tick mark corresponds to a natural number, starting from 1 and continuing indefinitely to the right. Here’s an example of how these numbers might be shown on a number line.
In this representation:
- Each number is placed at equal intervals along the line.
- The number 1 is usually positioned at the far left, indicating the starting point of the natural number sequence.
- Successive natural numbers are placed to the right of the previous one, each appearing one unit further along the line.
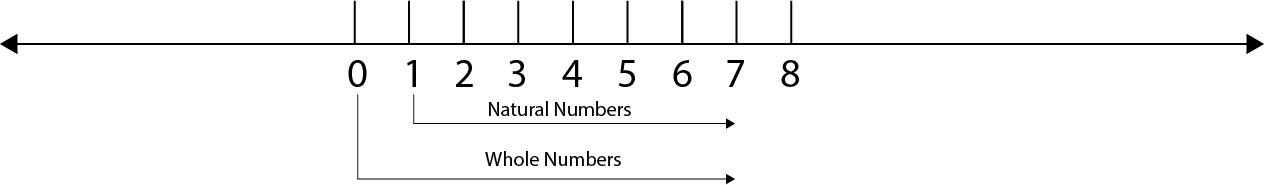
Properties of Natural Numbers
Closure Property:
The closure property of these numbers means that when we add or multiply any two natural numbers, the result is always another natural number.
Addition:3+5=8, which is also a natural number.
Multiplication: 4×6=24, which is also the same number.
Commutative Property
The commutative property of these numbers states that the order of numbers doesn’t affect the result of addition or multiplication. In other words, when we add or multiply two natural numbers, changing the order of the numbers doesn’t change the outcome.
For example:
- 2+3=3+2=5
- 4×5=5×4=20
Associative Property
The associative property of these numbers states that when performing addition or multiplication operations on three or more numbers, the grouping of the numbers does not affect the result.
For example:
- (2+3)+4=2+(3+4)=9
- (4×2)×3=4×(2×3)=24
Distributive Property
The distributive property of these numbers describes the relationship between addition and multiplication. It states that multiplication distributes over addition. In other words, when we multiply a number by the sum of two other numbers, it’s the same as multiplying the number by each of the other two numbers separately and then adding the results.
For example:
2×(3+4)=2×3+2×4
2×7=6+8
14=14
Classification of Natural Numbers
Even Numbers
A Natural Number is said to be even if it is divisible by 2.
Example: 2,4,6,8,10,12,…
Odd Numbers
A Natural Number is said to be odd if it is not divisible by 2.
Example: 1,3,5,7,9,11,…
Puzzle:
Count the spelling of even (4 which is even) Now
Count the spelling of odd (3 which is odd)
Prime Numbers
A Natural Number is said to be Prime if it has only two different factors namely one and itself.
Example:2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23 and so on.
2 is the only even prime number.
Composite Numbers
A natural number is considered composite if it has at least three factors.
Example: 4, 6,8,9,10.12 etc.
1 is neither a prime nor a composite number but a unit number.
Twin Prime
Two prime numbers are said to be twin primes if they differ by 2.
Example: (3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13), (17, 19), (29, 31), (41, 43), etc.
Prime triplet
A prime triplet is a set of three prime numbers in which the smallest and largest of the three differ by 6. For example (5,7,11) is a prime triplet.
Coprime numbers
Two numbers are said to be coprime if their HCF is 1, i.e only 1 as their common factor
Predecessor
The predecessor is known as before numbers (that appear just before) e.g
The predecessor of 9 is 8.
Successor
The successor is known as after numbers (that appear just after).
The successor of 5 is 6
FAQ
What is called natural number?
Natural numbers are a set of positive integers that start from 1 and extend indefinitely. They are commonly denoted by the symbol N or simply represented as 1,2,3,4,…Natural numbers also called Counting numbers.
Which is the largest Natural Number?
There is no largest Natural Number.
Is zero a natural number?
No, zero is not a natural number but it is the smallest whole number.
Which is the smallest Natural Number?
1 is the smallest Natural Number


