Introduction
Fractions are a fundamental part of mathematics. They represent parts of a whole. There are two parts in it. These parts are separated by a horizontal or diagonal bar. The number above the bar is called the numerator, and the number below the bar is called the denominator.
For example, 3/4:
3 is the numerator, indicating there are 3 parts.
4 is the denominator, indicating the whole is divided into 4 equal parts.
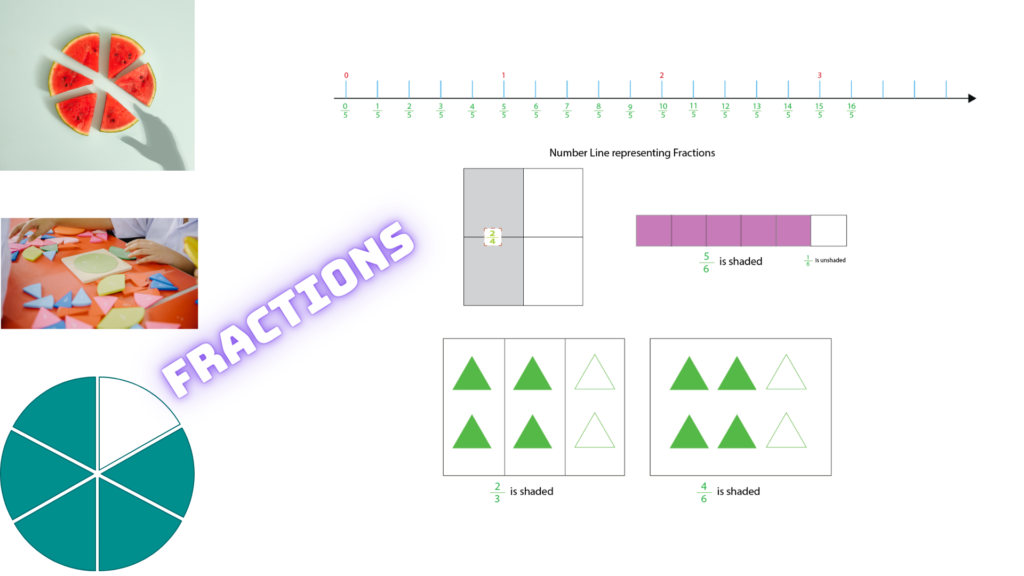
Definition of a Fraction
A fraction in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not equal to zero, is a basic representation of a fraction. This notation ensures that both the numerator (p) and the denominator (q) are whole numbers. It can represent a wide range of values, from very small like 1/100 to larger ones like 7/3
Types of a Fraction
Proper Fractions:
Proper fractions are those fractions in which the denominator is greater than the numerator. Example:1/4, 3/8, and 17/8
Improper Fractions:
Improper fractions are those fractions in which the denominator is greater than the numerator. Example: 15/4, 7/3, and 11/2 are all improper fractions.
Mixed Fractions:
Mixed fractions combine a whole number and a proper fraction. Example: 3 1/2, 5 3/4, and 3 4/5
Equivalent Fractions:
Equivalent fractions represent the same value but are written differently. For example, 1/2, 2/4, and 3/6 are all equivalent fractions because they represent the same portion of a whole.
Operations with Fractions:
Addition and Subtraction:
To add or subtract fractions, first, ensure they have the same denominator. Then, simply add or subtract the numerators while keeping the denominator unchanged.
- For example, 1/3 + 1/3 = 2/3. and 4/3 – 2/3 = 2/3.
Multiplication:
In the multiplication of fractions, we multiply the numerators to get the new numerator and multiply the denominators together to get the new denominator.
For example, 1/2 × 2/3 = 2/6.
Division:
In the division of fractions, we multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal second fraction.
- For example, 1/2 ÷ 1/3 is the same as 1/2 × 3/1 = 3/2.
Applications of Fractions:
Fractions have countless real-world applications, making them essential in various fields. Here are a few examples:
Cooking:
Recipes often require measurements in fractions, such as 1/2 cup of flour or 3/4 teaspoon of salt.
Construction:
Architects and builders use fractions to measure lengths, widths, and heights accurately.
Finance:
Fractions are used in finance to calculate interest rates, percentages, and investments.
Medicine:
Medical professionals use fractions to administer medication doses accurately.
Conclusion
Fractions may seem daunting at first, but with practice and patience, you’ll soon become proficient in working with them. Remember, fractions represent parts of a whole, and they’re all around us in everyday life. So the next time you encounter a fraction, whether it’s in a recipe, a measurement, or a math problem, embrace it with confidence. Fractions are your friends on the journey to mathematical master


