Introduction
Factors are like the DNA of numbers, the fundamental building blocks upon which mathematical structures are built. They play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts, from basic arithmetic to advanced algebra and beyond. Yet, despite their importance, factors can often be misunderstood or overlooked. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of factors, unraveling their significance and exploring their applications.
Definition
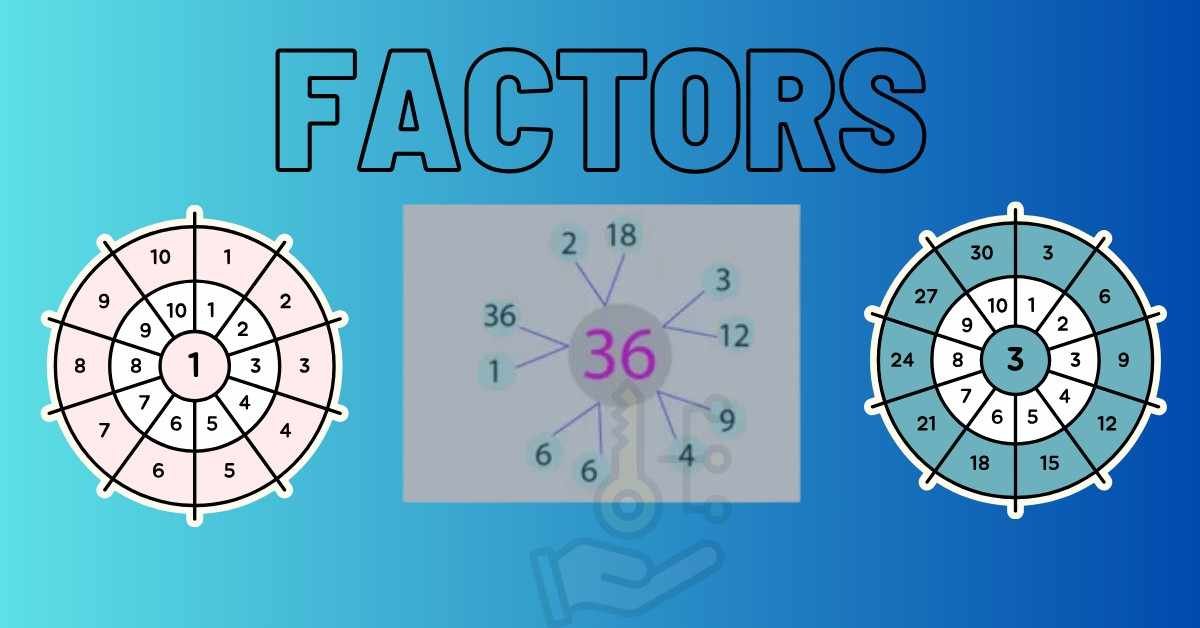
Factors are the numbers that can be multiplied together to make a bigger number For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because these numbers can all be multiplied together in pairs to equal 12:
1 × 12 = 12
2 × 6 = 12
3 × 4 = 12
Factors are intimately tied to the concept of division. If a number 𝑎 can be divided by another number 𝑏 without leaving a remainder, then 𝑏 is a factor of 𝑎. This relationship forms the basis of many mathematical operations and principles.
Expanded Form
Factors are used to expand numbers under multiplication operation. In the given highlighted table various natural numbers are expanded to understand such expansion.
Understanding Prime Factors
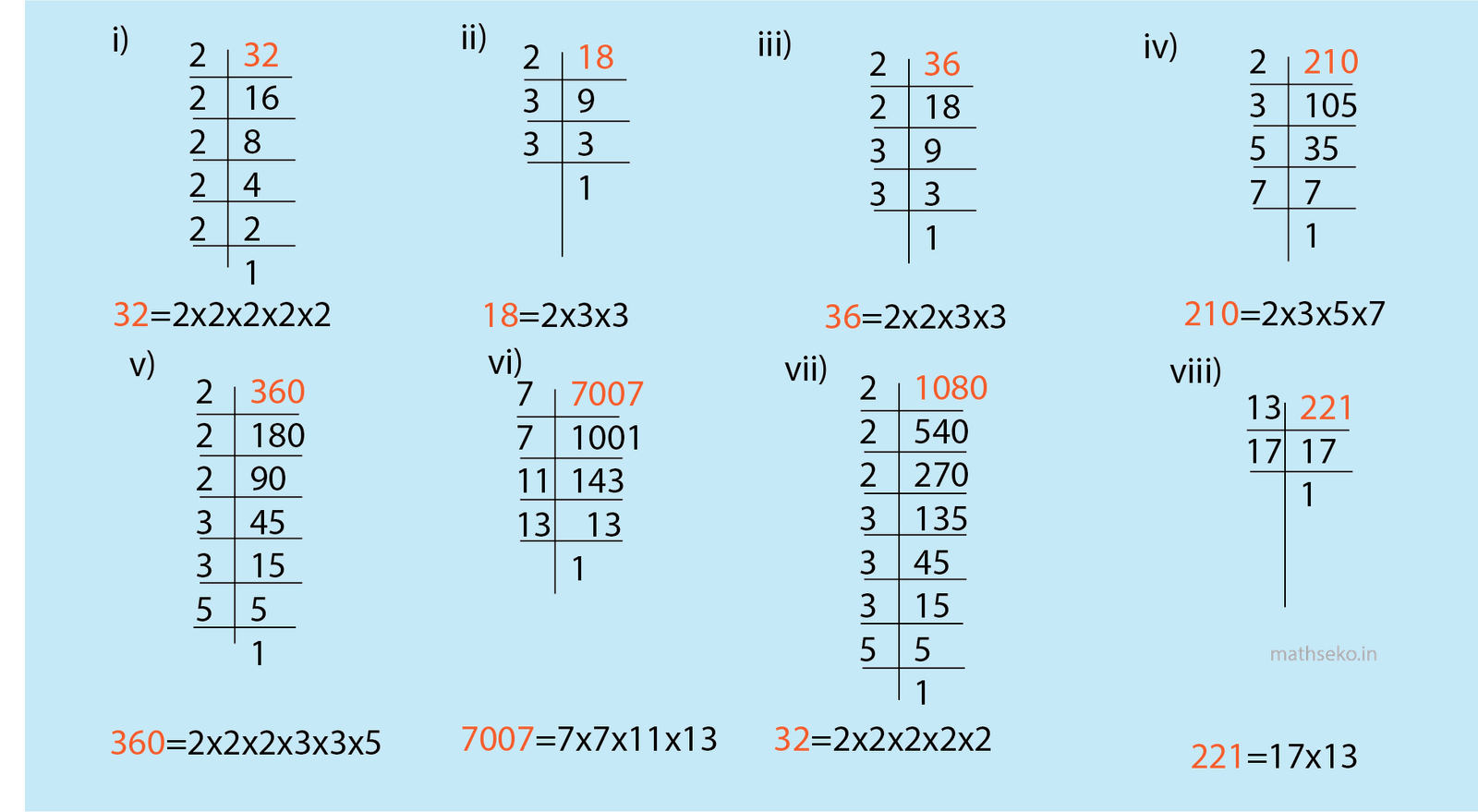
Prime factors hold a special place in the realm of factors. A prime factor is a factor that is also a prime number, meaning it has exactly two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. .For example , the prime factors of 12 is 2x2x3
Imagine you have a big number, like 12. Prime factorization is like finding the simplest pieces that make up that number. For 12, the simplest pieces are 2 and 3. We call these “prime numbers” because they can’t be broken down into smaller parts. It’s like finding the smallest building blocks in a big Blog set. Knowing these small blocks helps us solve puzzles and even unlock secret codes!
So, prime factorization is like discovering the tiny, unbreakable pieces hidden inside big numbers. It’s like being a detective, finding clues to solve mysteries in math and beyond!
Prime factorization is not only a fundamental concept in number theory but also forms the backbone of various cryptographic algorithms and factorization techniques used in computer science and cryptography.
Applications of Factors
Their applications in numerous areas of mathematics and real-world problems:
1. Number Theory
Factors are central to many number theoretic problems, such as finding the highest common factor (HCF) or the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers.
2. Algebra
In algebra, factoring polynomials involves breaking them down into their constituent factors, which is essential for solving equations and simplifying expressions.
3. Cracking hidden messages:
Understanding the prime factors of large numbers helps decode secret messages, such as those used to protect sensitive information, like the ones used to keep messages safe. This is super important in computer security, where we need to keep information private..
4. Economics and Finance
Factors play a role in financial mathematics, where they are used in formulas for compound interest, Regular Payments, and investment analysis.
5. Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, factors are used in various calculations, such as determining the forces acting on an object or analyzing circuits.
Importance
These are like math’s secret helpers, quietly solving all sorts of problems. Understanding them makes us better at math and helps in solving many different kinds of problems. Whether you’re having trouble with math or working on cool things like keeping secrets safe online, knowing about factors is really important. So, next time you see a number, think about its factors—they’re the key to unlocking its secrets and understanding it better in math
FAQ
- A factor in mathematics refers to a number that divides another number evenly without leaving a remainder. For example, factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because they divide 12 evenly.
A prime factor is a factor of a number that is a prime number itself. In other words, it is a prime number that divides the given number exactly without leaving a remainder.
A prime factor is a factor that is a prime number, while a composite factor is a factor that is a composite number (a number that is not prime). For example, in the number 12, the prime factors are 2 and 3, while the composite factors are 4 and 6.
To find the factors of a number, you can divide the number by each integer starting from 1 up to the number itself. The numbers that divide the given number without leaving a remainder are its factors.
The smallest factor of a number is 1, and the largest factor is the number itself. Every number is divisible by 1, and every number is also divisible by itself.
Yes, a number can have more than two factors. For example, 12 has six factors: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
If a number has exactly two factors (1 and itself), it is a prime number. If a number has more than two factors, it is a composite number.
Factors are numbers that divide another number evenly, while multiples are the result of multiplying a number by an integer. Factors and multiples are related because they are opposite operations. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, and the multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, etc.
Prime factorization involves expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. This is done by repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factors until all factors are prime. For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 × 2 × 3.
Prime factorization is important in mathematics because it helps simplify calculations, find common factors and multiples, and solve problems related to factors and multiples.